Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Trigonometry - non-right angled triangles.
Cosine Rule - introduction.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
As noted previously, the Cosine Rule is an equation linking three angles and one side in a triangle. Any question involving the applcation of the Cosine Rule will give you three of these four measurements and ask you to determine the fourth - whether that be the angle or one of the sides.
The proof of the relationship amongst the sides and the angle - so the "formula" - is as follows:
 |
Draw a triangle. Mark the three vertices as A, B and C. Label the three sides using the lower case letter from the angle opposite. Drop a vertical from the apex perpendicular to the side opposite and mark its height as h. Mark the distance from vertex A to the vertical with the distance x and so the balance of that side has the length of (b - x). |
| Write down the Pythagorean equations for the two triangles with the right angles using h as the subject: | 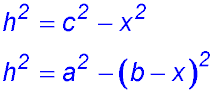 |
| Equate the two equations and simplify to make x the subject. | 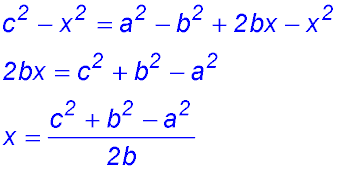 |
| Write down the usual equation for cos A, substitute and simplify | 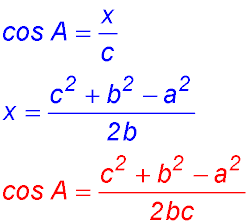 |